What
is Automotive Warranty Management?
Warranty management is the process
of handling vehicle repair claims when a car part fails within a
specific period. A well-managed warranty system helps:
✔ Reduce costs for automakers
and suppliers.
✔ Improve customer satisfaction
by resolving issues quickly.
✔ Prevent future problems by
identifying defects early.Auto Genius provides OEMs an advanced warranty management software to manage their automotive warranties effectively. 
📌 Example: Imagine
you buy a new car, and after six months, the air conditioning stops working. If
the car is still under warranty, the dealer will repair or replace the faulty
part for free. But if warranty claims are not handled properly, delays
and confusion can frustrate customers.
Who
is Responsible for the Warranty Process?
Many people are involved in handling
warranty claims:
1️ Car Manufacturer (OEM - Original Equipment Manufacturer)
- Creates warranty policies and guidelines.
- Works with suppliers and dealers to process claims.
- Ensures quality control in car manufacturing.
2️ Suppliers (Parts Manufacturers)
- Provide high-quality parts and components for
vehicles.
- Help investigate why a part failed.
- Assist in reducing warranty claims by improving their
products.
3️ Dealers (Car Showrooms & Service Centers)
- First contact point
for customers facing problems.
- Diagnose the issue and decide whether the repair falls
under warranty.
- Communicate with manufacturers and suppliers to fix the
problem.

How
to Handle Warranty Claims Efficiently?
When a part fails, the company must
follow a clear and structured process to fix it. Key best practices
include:
✔
Documented Warranty Policies – Both internal teams and suppliers should
have a step-by-step guide on how to handle claims.
✔
Regular Training for Dealers & Suppliers – Proper training ensures
that warranty claims are processed correctly and fairly.
✔
Easy Access to Warranty Data – Companies should have online portals
where suppliers can see warranty claim records. This helps in faster
investigations.
🔍
Example: If multiple cars have the same brake issue, an online
system will help identify the problem faster. The supplier can then analyze
and improve the brake design to prevent future failures
Importance
of Warranty Data and Online Portals
Manufacturers and suppliers need detailed
data to investigate warranty claims properly. This data includes:
📌 Dealer Reports – What problem the
customer reported, what was repaired, and whether the issue was solved.
📌 Vehicle Data – Information collected from car sensors
and onboard diagnostic systems.
📌 Warranty History – Records of past repairs and similar issues
in other vehicles.
💡 Best Practice:
Automakers should create easy-to-use online portals where suppliers can
check warranty data, download reports, and analyze failure patterns.
How
to Return and Analyze Defective Parts?
To truly understand why a part
failed, companies must examine the defective component. But not all parts
can be sent back for review due to high costs. Instead, manufacturers
should:
✔
Decide which parts to return based on the issue type.
✔ Hold monthly review meetings
to check faulty parts.
✔ Use video meetings so that
remote teams can also inspect defects.

📌 Example: If fuel
pumps in a certain model are failing too often, collecting some defective
pumps from dealerships will help suppliers find out if the issue is due to poor
material quality or incorrect installation.
Reducing
Warranty Costs: What Are the Main Issues?
Warranty claims cost millions of
dollars each year. The biggest cost drivers are:
1️ Manufacturing Mistakes – If a factory assembles
parts incorrectly, they may fail early.
2️ Wrong Repairs by Dealers – Sometimes, the real issue is not fixed,
causing repeat claims.
3️ "No Trouble Found" (NTF) Cases – When a car is brought for
repair, but technicians can’t find anything wrong, the issue remains
unsolved.
💡 Best Practice:
✔ Train employees in correct
assembly and repair techniques.
✔ Use advanced data analysis
to detect patterns in failures.
What
is a Fair Cost Recovery System?
When a part fails under warranty, who
should pay for the repair?
- If a supplier made a faulty part, they should cover
the costs.
- If a manufacturer installed it incorrectly, they
should pay.
- If the problem is unclear, both parties should investigate
and share the costs fairly.
📌 Best Practice: A clear,
documented process should be in place to decide who is responsible
for each claim.
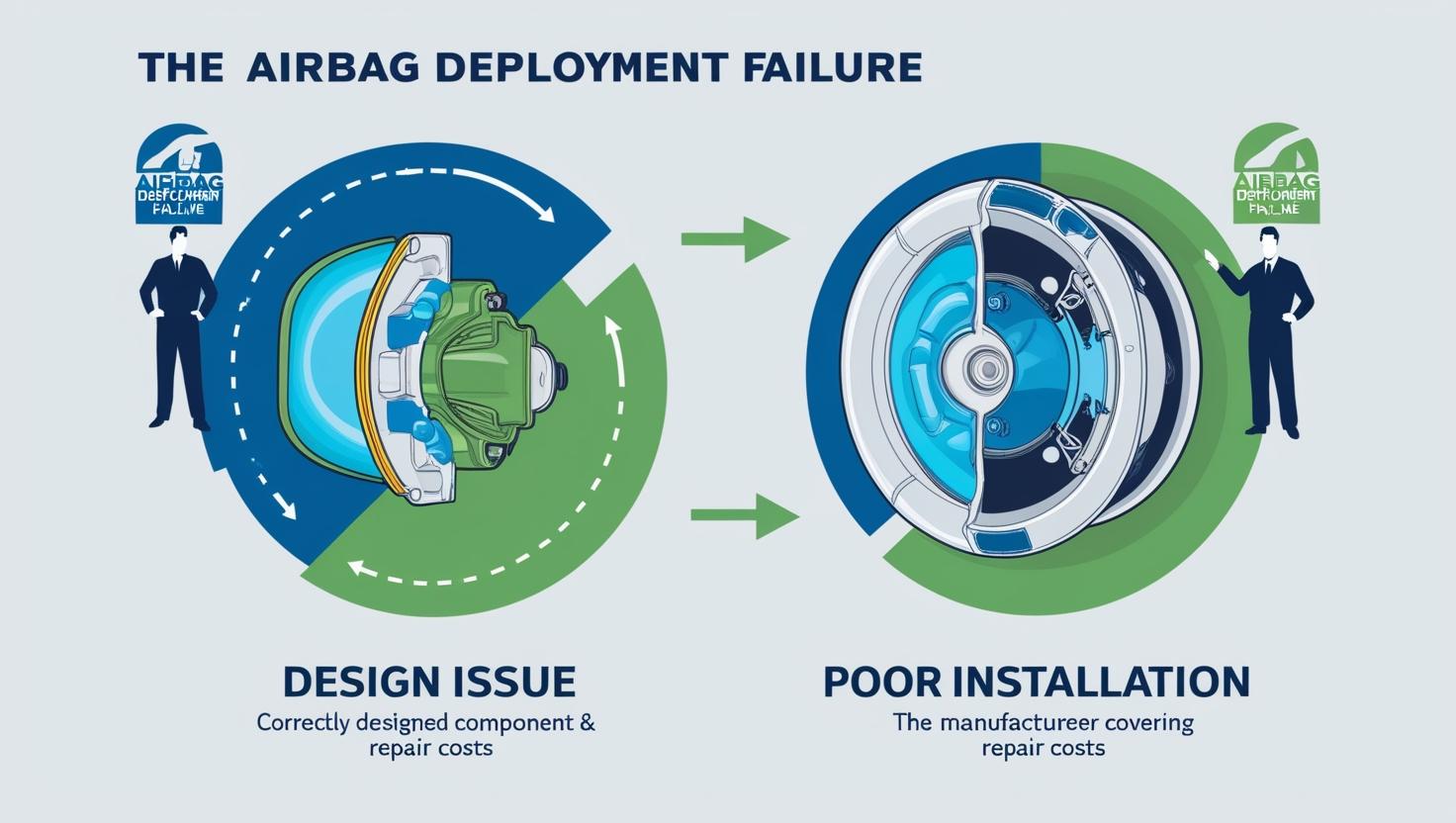
🚗 Example: If an
airbag fails due to a design issue, the supplier may cover the repair
cost. But if it fails due to poor installation at the factory, the
manufacturer should pay.
How
Technology Can Improve Warranty Management?
With modern technology, companies
can prevent warranty issues before they happen:
📊 Data Analytics –
Helps detect failure patterns before a problem becomes widespread.
📡 Car Sensors & Telematics – Collects real-time data about
how a car is performing.
🛠 Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Helps analyze customer
complaints and identify common defects.
✅ Example:
A car manufacturer notices that engine temperature sensors in a
certain model fail after 50,000 miles. By analyzing data from multiple
vehicles, they can recall and replace sensors before a serious issue
occurs.
Building
Strong Relationships Between Manufacturers, Suppliers, and Dealers
Many warranty issues happen because dealers,
manufacturers, and suppliers don’t communicate properly. To improve
relationships:
✔
Encourage dealers to share more details when submitting claims.
✔ Give suppliers full access
to warranty data so they can investigate issues faster.
✔ Allow dealers to contact
suppliers directly for technical support.
📌
Example: A car dealership struggles to repair a complicated electronic
braking system. Instead of waiting for slow responses from the
manufacturer, they call the supplier directly for help.
What
Happens in the Future?
As vehicles become more advanced,
warranty management will become more complex.
🚗 Electric Vehicles (EVs)
have different failure patterns compared to gasoline cars.
🔌 Self-driving technology will need new warranty rules for software
failures.
📡 Subscription-based car models (where people don’t own cars but
rent them monthly) will create new challenges in warranty policies.
The best
companies will be those that create flexible and data-driven
warranty systems to adapt to these future challenges.
This guide provides a clear,
step-by-step approach to managing automotive warranties effectively. By
using data, technology, and collaboration, manufacturers, suppliers, and
dealers can reduce costs, prevent failures, and keep customers happy.